Difinition of lungs , Anotomy,cause of lungs disorders, symptoms, functions, condition, treatment and test s
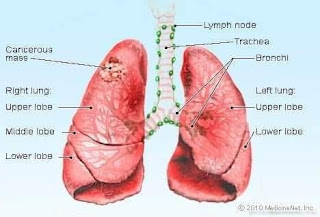
Definition of Lung, Anatomy,Causes of lung disorders, Symptoms, Function,Conditions, Treatment and tests. The lungs are a pair of spongy, air-filled organs located on either side of the chest (thorax). The trachea (windpipe) conducts inhaled air into the lungs through its tubular branches, called bronchi. The bronchi then divide into smaller and smaller branches (bronchioles), finally becoming microscopic. The bronchioles eventually end in clusters of microscopic air sacs called alveoli. In the alveoli, oxygen from the air is absorbed into the blood. Carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, travels from the blood to the alveoli, where it can be exhaled. Between the alveoli is a thin layer of cells called the interstitium, which contains blood vessels and cells that help support the alveoli. The lungs are covered by a thin tissue layer called the pleura. The same kind of thin tissue lines the inside of the chest cavity -- also called pleura. A thin layer of fluid acts as a lu...

